Share the post "NAZI Rocket Scientist to NASA: The Riveting Journey of Wernher von Braun"
Wernher von Braun is one of space exploration’s most mysterious and influential figures. Science, ambition, and controversy shaped his rise from Nazi rocket engineer to NASA’s moon landing leader. We examine his life, which was characterized by technological advancements and moral dilemmas related to his involvement with the Nazis during World War II.
Ingenuity and technical expertise helped von Braun develop the V-2 rocket for Germany, a technological marvel with a dark side as a weapon of war. His expertise made him invaluable in the space race against the Soviet Union despite his past affiliations. His transition from working for the Third Reich to leading America’s lunar ambitions shows the Cold War’s fascinating mix of ethics and pragmatism.
Our investigation shows how von Braun’s Saturn V rocket design enabled Apollo 11’s moon landing. Many dreamed of this moment, which propelled von Braun to international fame and reignited wartime discussions. We discover the complex life of Wernher von Braun, whose impact on our journey to the stars is impressive and disputed.

Early Life of Wernher von Braun
Wernher von Braun had an aristocratic upbringing, a love of rocketry, and contentious affiliations in his early years, which we are about to reveal.
Childhood and education
Wernher von Braun was born into aristocratic prosperity on March 23, 1912, in Wirsitz, Germany, now known as Wyrzysk, Poland. Our exploration begins with his early fascination with the cosmos, which solidified when he received a telescope as a confirmation gift. He pursued this passion academically, eventually earning a Ph.D. in physics from the University of Berlin in 1934.
Initial rocket experiments
From an early age, von Braun showed exceptional interest in space and rocketry. He became involved with the German rocketry association VfR (Verein für Raumschiffahrt), where he conducted his initial rocket experiments. These practical experiences laid the groundwork for his eventual monumental contributions to German and American space efforts.
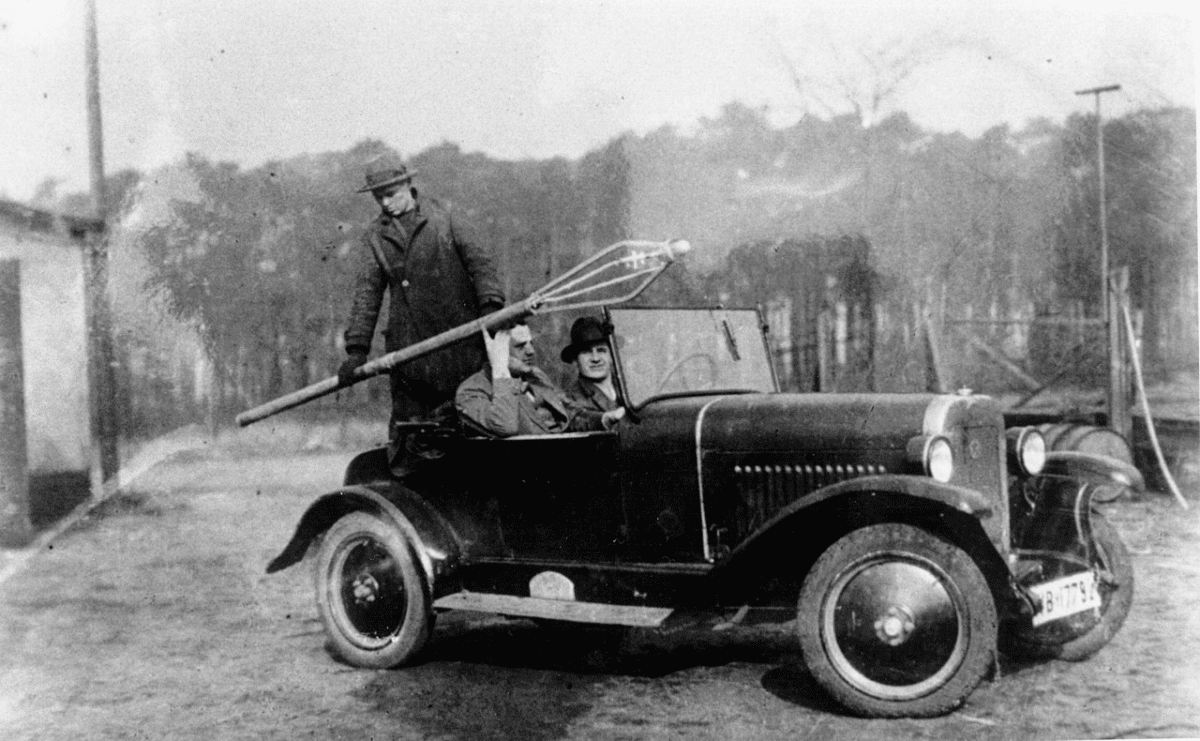
Rise through the Nazi ranks.
von Braun’s began to rise through the ranks of the Nazi regime. After joining the Nazi Party in 1937 and later the SS, he became instrumental in Germany’s rocket development program during World War II. Despite these affiliations’ complex and troubling nature, they played a critical role in his career trajectory, ultimately leading him to NASA.
Each step in von Braun’s early life, from his nobility-tinged childhood and rigorous education to his pioneering rocketry efforts, was a stepping stone leading to groundbreaking advancements in space exploration—though not without the moral and ethical complexities we continue to grapple with today.

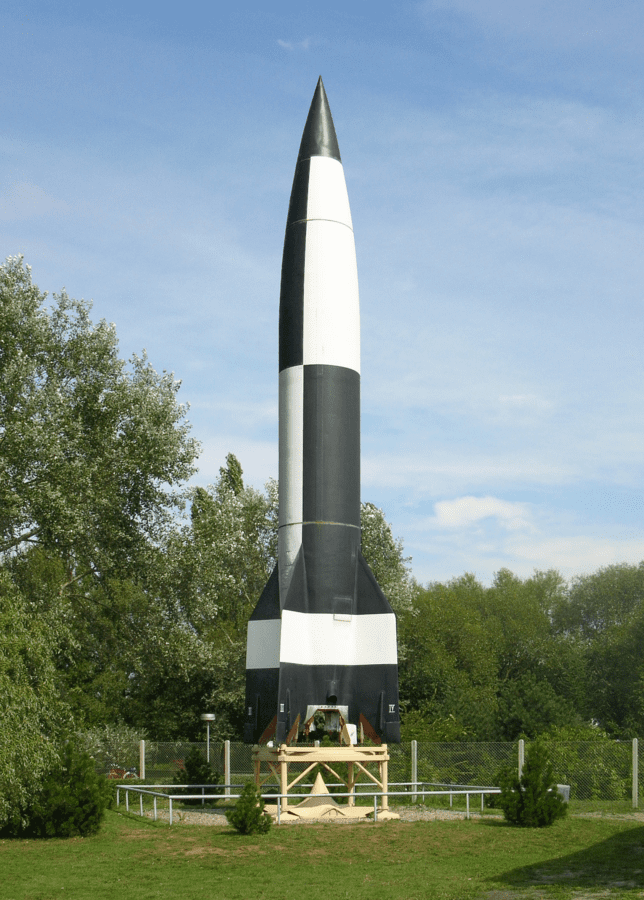
World War II and the V-2 Rocket
During World War II, we witnessed revolutionary advancements in rocket technology. One of the most significant was the development of the V-2 rocket, which had a substantial impact on the war and laid the foundation for future space exploration.
Development of the V-2 Rocket
In the early 1940s, we saw the birth of the V-2 rocket, the world’s first long-range guided ballistic missile. The brain behind this pioneering technology was Wernher von Braun, a scientist who dreamt of space exploration but found himself developing weaponry. A significant improvement over earlier solid-fuel rockets was using a liquid-propellant engine in this rocket.
Production and Impact on the War
The production of the V-2 was a monumental effort. From 1942 to 1945, an estimated 6,000 V-2s were manufactured. These rockets were primarily aimed at Allied cities, causing destruction and alarm. The ruthless efficiency of these weapons highlighted the terrifying potential of missile technology in warfare—a potential that was not lost on the world.
Ethical Controversies
However, severe ethical problems plagued the production of the V-2 rocket. The conditions of forced labor were appalling. Thousands of concentration camp prisoners were put to work in the underground production facilities, and many lost their lives due to the inhumane treatment they received. This dark chapter of the V-2 rocket reveals the harrowing intersection between technology and human rights violations during World War II.

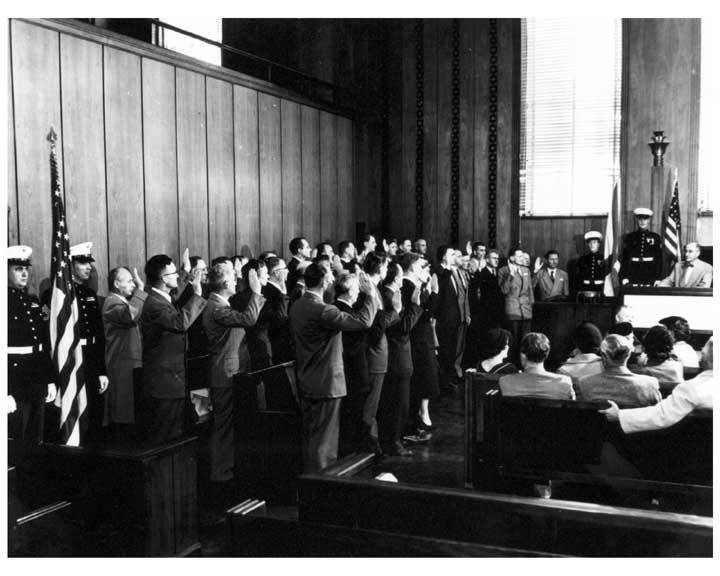
Surrender and Operation Paperclip
In the twilight of World War II, Wernher von Braun decided to shape his future and the course of space exploration. Our focus now turns to his surrender to American forces and his subsequent involvement in Operation Paperclip.
Decision to Surrender to Americans
Wernher von Braun, sought to secure a future by submitting to the Americans rather than the Soviets as Nazi Germany faced inevitable defeat. He approached American forces in Austria in the spring of 1945 due to his desire to continue scientific research in the post-war era.
Role in Operation Paperclip
After his surrender, he became integral to Operation Paperclip, a secret U.S. intelligence program that transported more than 1,600 German scientists, us included, to the United States. There, we played a vital role in the development of the U.S. ballistic missile program and, eventually, the space program, leveraging our expertise as former Nazi rocket scientists to advance American technological supremacy during the Cold War.

Contributions to American Spaceflight
Wernher von Braun’s recruitment to America as part of Operation Paperclip was a pivotal moment in the history of space exploration. His expertise would lead to critical advancements in pursuit of the stars.
Joining NASA
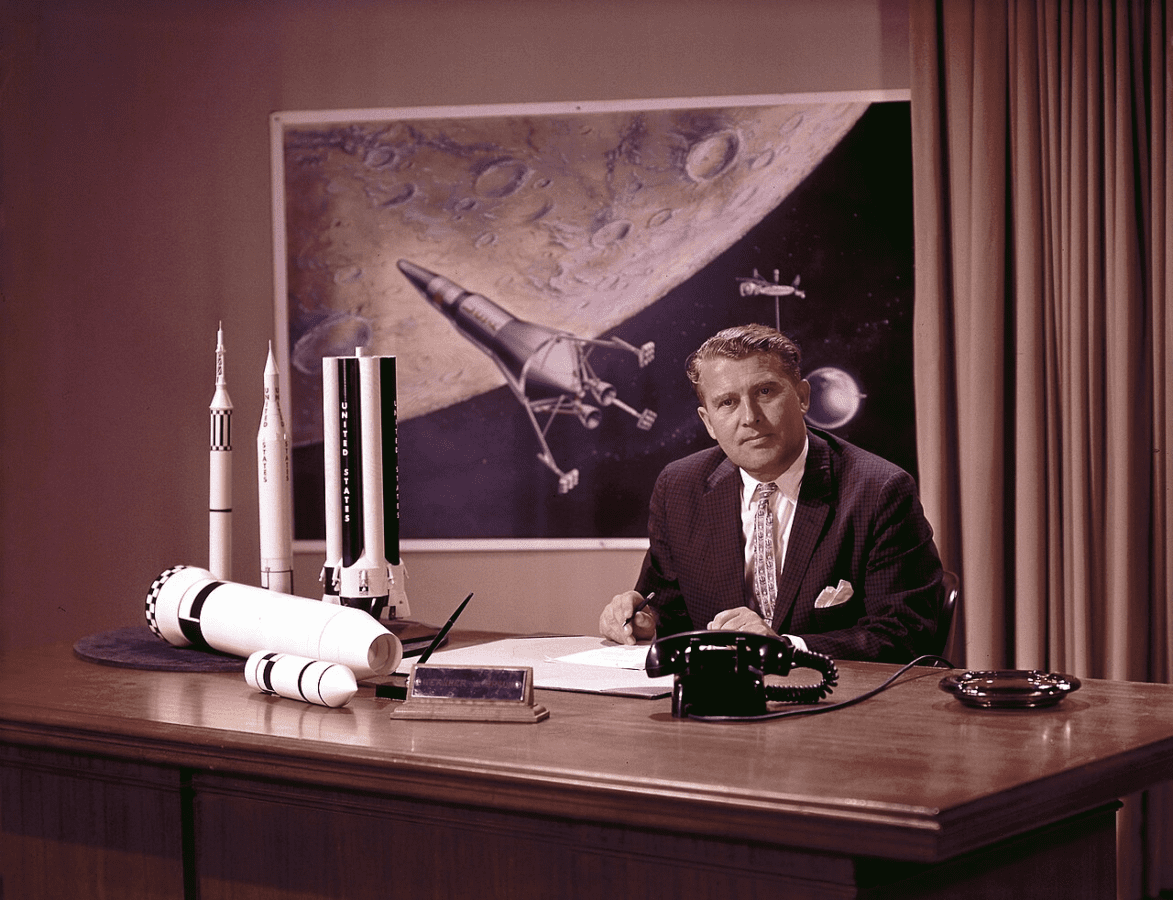
After his initial work with the Army Ballistic Missile Agency, we welcomed von Braun’s transition to the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) in 1960. His leadership and expertise were instrumental in establishing Project Mercury, America’s first human spaceflight program. This positioned us to compete in the space race.
Saturn V and Apollo Missions
Saturn V, the rocket that symbolizes a leap to the lunar surface, which was the brainchild of von Braun and his team. It was a giant leap in our technological capabilities and remains the most powerful rocket ever successfully flown. This incredible innovation powered the Apollo missions, including the historic Apollo 11, culminating in humanity’s first steps on the Moon. The success of these missions marked a series of unparalleled achievements in spaceflight that expanded our horizons and our understanding of what’s possible.
Legacy and Controversies
Wernher von Braun’s story is an entwined tale of scientific triumph and historical complications. His contributions revolutionized space exploration, yet his past raises moral debates.
Impact on Space Exploration
We can proudly look at the Saturn V rocket as a towering testament to human ingenuity and evidence of von Braun’s impact on space exploration. As the chief architect of the rocket that propelled the Apollo missions, von Braun is often hailed as the “father of rocket science.” Without him, our moon conquest might have remained a mere fantasy.
Debate Over His Past
Yet, the celebration is complex when we examine von Braun’s affiliations during World War II. With a past inextricably linked to Nazi Germany and the V-2 rocket—a weapon responsible for thousands of deaths—his legacy is shrouded in questions of ethics and justice. There remains an ongoing debate over his past, as the moral implications of utilizing his expertise during the Cold War continue to provoke discussion and reflection.
Share the post "NAZI Rocket Scientist to NASA: The Riveting Journey of Wernher von Braun"
Christian Linden is a seasoned writer and contributor at Texas View, specializing in topics that resonate with the Texan community. With over a decade of experience in journalism, Christian brings a wealth of knowledge in local politics, culture, and lifestyle. He holds a Bachelor's degree in Communications from the University of Texas. When he's not writing, Christian enjoys spending weekends traveling across Texas with his family, exploring everything from bustling cities to serene landscapes.











